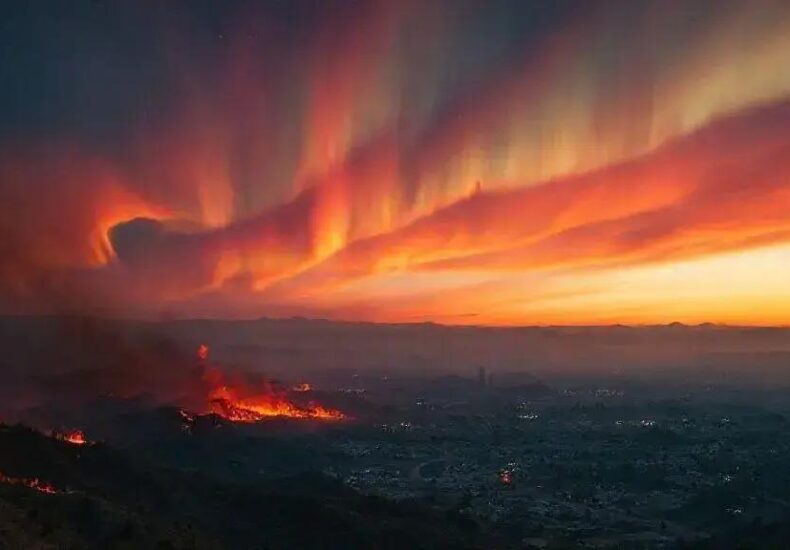

Solar Storm Influence Los Angeles Fire: What You Need to Know
Solar storms influence Los Angeles fire risks by disrupting electrical grids, communication systems, and weather patterns, which can increase wildfire chances and complicate firefighting efforts.
Solar Storm Influence Los Angeles Fire is a topic gaining attention as researchers and locals alike wonder if solar activity could affect wildfire risks. Ever considered how storms from space might tangle with fires on the ground? Let’s unpack what we know so far.
understanding solar storms and their origins
Solar storms, also known as geomagnetic storms, originate from the sun’s intense activities such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections. These bursts release massive amounts of charged particles and electromagnetic radiation into space. When directed towards Earth, they interact with the planet’s magnetic field, creating vivid auroras and sometimes disrupting satellites, communications, and power grids.
What Causes Solar Storms?
The sun’s magnetic field is constantly shifting. Occasionally, energy builds up and releases suddenly in the form of solar flares. Coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are huge bubbles of gas threaded with magnetic field lines that shoot out from the sun’s corona. Both solar flares and CMEs cause solar storms.
How Solar Storms Develop
Once released, charged particles travel at millions of miles per hour. When these particles collide with Earth’s magnetosphere, they cause disturbances that can last from several hours to days. The strength of a solar storm depends on the sun’s activity cycle, peaking about every 11 years.
Understanding these origins helps us predict when solar storms might impact Earth and prepare accordingly. Advances in space weather forecasting equip researchers and governments to monitor solar activity and mitigate risks associated with strong storms.
how solar storms interact with earth’s magnetic field
When solar storms reach Earth, they interact with the planet’s magnetic field, known as the magnetosphere. This magnetic shield protects us by deflecting charged particles from the sun. However, strong solar storms can disturb this field, causing geomagnetic disturbances.
The Role of Earth’s Magnetic Field
Earth’s magnetic field extends thousands of miles into space, creating a protective bubble. When charged particles from a solar storm hit this field, they can cause it to bend and fluctuate. These changes in the magnetosphere create currents and magnetic storms that impact technology and the environment.
Effects of Interaction
One key effect is the generation of auroras, colorful lights seen near the poles. The charged particles excite atoms in the atmosphere, causing them to glow. However, this interaction can also disrupt satellites, GPS signals, and even power grids on the ground.
Scientists monitor the magnetosphere closely to predict these disturbances. Improving our understanding helps protect communication networks and electrical systems from potential damage caused by solar storms.
historical solar storms and their impacts
Throughout history, solar storms have caused significant effects on Earth’s technology and environment. One of the most famous events is the Carrington Event of 1859, which was the strongest geomagnetic storm recorded. It disrupted telegraph systems worldwide and produced spectacular auroras visible near the equator.
Major Historical Solar Storms
Other notable storms include the March 1989 Quebec blackout, where a solar storm caused a power outage affecting millions of people for several hours. This event highlighted how vulnerable electrical grids can be to strong geomagnetic activity.
The Halloween Storms of 2003 triggered disruptions in satellite operations, radio communications, and posed risks to astronauts in space. These storms also caused minor damage to power systems and increased radiation exposure.
Long-Term Impacts
Historical solar storms reveal the potential for widespread technological disruption. These events emphasize the need for robust monitoring and protective measures to reduce risks to infrastructure like satellites, GPS systems, and power grids during future storms.
mechanisms linking solar storms to fire risk
Solar storms affect Earth by releasing high-energy particles and causing geomagnetic disturbances. These events can indirectly contribute to fire risk, especially in areas like Los Angeles that are already prone to wildfires. The key connection lies in how solar storms can disrupt electrical systems and influence weather.
Electrical grid vulnerabilities
Strong solar storms induce powerful electric currents in power lines and transformers. This can cause equipment failures and widespread power outages. Without electricity, fire prevention systems such as pumps and alarms may fail, increasing the likelihood of uncontrolled fires.
Weather and atmospheric effects
Solar storms can influence Earth’s upper atmosphere, sometimes affecting wind patterns and humidity levels. Changes in these conditions can create drier and windier environments, which are perfect for sparking and spreading wildfires.
Communication and monitoring disruptions
Solar storm-induced disruptions to satellite communications and GPS can hinder firefighting efforts. When communication systems fail, coordinating emergency responses and detecting new fires becomes more difficult, increasing fire risks.
Understanding these mechanisms is vital for preparing fire-prone regions against combined threats from solar storms and wildfires.
climate conditions in los angeles relevant to fires
Los Angeles has a Mediterranean climate characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. These weather patterns create conditions that are often ripe for wildfires, especially during late summer and fall.
Seasonal Weather Patterns
During the summer, temperatures often soar above 90°F, causing dry vegetation to become highly flammable. The lack of rain at this time means that moisture levels in the soil and plants drop significantly.
Santa Ana Winds
One of the most important factors affecting fires in Los Angeles is the Santa Ana winds. These strong, dry winds blow from the inland desert toward the coast, raising temperatures and lowering humidity. They can reach speeds over 60 mph, quickly spreading any existing fires and making firefighting efforts difficult.
Drought and Vegetation
Extended drought periods have weakened vegetation, making it easier for fires to ignite and spread. The dry brush and chaparral native to the region act as natural fuel, intensifying wildfire behavior.
Understanding these climate conditions in Los Angeles is crucial for predicting fire risk and implementing effective prevention strategies.
recent fire incidents in los angeles and contextual factors
Los Angeles has faced several significant fire incidents in recent years, each influenced by a mix of natural and human factors. Notable fires like the Woolsey Fire in 2018 and the Saddleridge Fire in 2019 caused widespread damage and evacuations.
Factors Contributing to Fire Incidents
Dry conditions and strong winds played a major role in spreading these fires quickly. The Santa Ana winds especially accelerated flames and increased fire unpredictability.
Urban expansion into wildland areas, known as the wildland-urban interface, also increases fire risks. Homes built near natural vegetation become vulnerable to rapid fire spread.
Human Activity and Climate
Human activities, including accidental ignitions and power line failures, have contributed to starting some fires. At the same time, long-term drought and rising temperatures due to climate change have made the environment drier and more fire-prone.
These recent fires show how multiple contextual factors combine to create dangerous conditions in Los Angeles. Awareness of these elements can help improve prevention and emergency response plans.
technological vulnerabilities during solar storms
Solar storms can expose several technological vulnerabilities on Earth, disrupting critical systems that society depends on daily. These storms release charged particles and electromagnetic radiation that interfere with electronic and communication technologies.
Impact on Power Grids
One major vulnerability is electrical power grids. Geomagnetic induced currents caused by solar storms can overload transformers and circuits, leading to blackouts. These failures can affect millions and require costly repairs.
Satellite and Communication Systems
Satellites orbiting Earth are highly susceptible to solar radiation. Solar storms can damage satellite electronics, affect onboard sensors, and disturb signals. This results in GPS inaccuracies, degraded phone and internet services, and impaired weather forecasting.
Aviation and Navigation
Solar storms also impact aviation by disrupting high-frequency radio communications and navigation systems at high altitudes and polar routes. Pilots may experience communication blackouts or loss of navigation precision during severe storms.
Understanding these technological weaknesses is essential for developing resilient systems and minimizing disruptions during future solar storms.
effects of solar storms on electrical infrastructure
Solar storms can have serious effects on electrical infrastructure. When charged particles from the sun reach Earth, they induce electric currents in power lines and transformers. These geomagnetically induced currents can overload and damage vital components.
Transformer Damage and Failures
Transformers are particularly vulnerable during solar storms. Excess currents can cause overheating, leading to permanent damage or failure. Repairing or replacing transformers requires time and significant cost, often resulting in power outages.
Power Grid Instability
The electric currents caused by solar storms can create voltage fluctuations and instability in power grids. This may trigger protective shutdowns to avoid equipment damage but can also leave large areas without electricity until the system stabilizes.
Wider Impacts
Damage to electrical infrastructure disrupts everyday life, affecting homes, businesses, and emergency services. In regions prone to wildfires like Los Angeles, power outages can impede firefighting efforts and increase overall fire risk.
Understanding these impacts helps utilities prepare for solar storms and implement measures to protect critical electrical infrastructure.
early warning systems for solar storms
Early warning systems are crucial for detecting solar storms before they impact Earth. These systems rely on satellites and ground-based observatories to monitor solar activity continuously.
Space-Based Solar Monitoring
Satellites like the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) track solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) in real time. They provide data on the speed and direction of charged particles heading toward Earth.
Ground-Based Observation Networks
Ground stations use magnetometers and radio telescopes to detect changes in Earth’s magnetic field and radio waves emitted by solar activity. These networks complement satellite data and enhance prediction accuracy.
Alert Systems and Preparedness
When a solar storm is detected, space weather centers issue warnings to governments, utility companies, and aviation authorities. These alerts allow for timely responses such as adjusting satellite operations, protecting power grids, and rerouting flights.
Continuous improvements in these early warning systems help reduce the risks associated with solar storms and protect critical infrastructure.
firefighting challenges posed by solar storms
Solar storms pose significant challenges to firefighting efforts, especially during large wildfire situations. The electromagnetic interference caused by these storms can disrupt communication systems, making coordination difficult among firefighting teams.
Communication Disruptions
Radio signals and satellite communications are often affected by solar storms. This hampers the ability of firefighters to relay information quickly and safely, slowing down response times and complicating strategy adjustments in rapidly changing fire conditions.
Technology Malfunctions
Equipment such as drones, GPS devices, and command center electronics can malfunction or lose accuracy due to solar storm interference. This reduces the effectiveness of tracking fires, mapping safety zones, and deploying resources efficiently.
Power Outages and Resource Limitations
Solar storms can cause power grid failures that impact water pumping stations and emergency services. Without reliable electricity, firefighting infrastructure weakens, leading to challenges in accessing water supplies and maintaining critical support systems.
Preparing for these challenges requires robust backup systems, alternative communication methods, and awareness of solar storm forecasts to minimize impact on firefighting operations.
how solar storms could influence weather patterns
Solar storms can have subtle effects on Earth’s weather patterns by disturbing the ionosphere and affecting atmospheric conditions. These changes can influence temperature, cloud formation, and even precipitation.
Atmospheric Heating and Circulation
When charged particles from solar storms enter the upper atmosphere, they can cause localized heating. This affects wind currents and jet streams, potentially altering weather patterns at lower altitudes.
Cloud Formation and Precipitation
Solar activity may impact cloud nucleation processes. Changes in cosmic ray intensity during solar storms can influence how clouds form, affecting rainfall distribution and intensity in some regions.
Potential Effects on Extreme Weather
While research is ongoing, there is some evidence that solar storms can correlate with shifts in extreme weather events like storms and droughts. These effects are complex and depend on various environmental factors.
Understanding how solar storms influence weather helps scientists improve forecasting models and prepare for potential climate impacts.
scientific studies on solar storms and fires
Scientific studies on solar storms and fires explore the complex relationship between space weather events and terrestrial fire activity. Researchers investigate how solar storms influence climate and environmental conditions that may affect wildfire risks.
Research on Solar Activity and Climate Effects
Studies show solar storms can alter atmospheric ionization and circulation patterns, which might lead to changes in temperature, precipitation, and wind behavior. These factors are critical in determining wildfire likelihood and behavior.
Correlating Solar Storms with Fire Incidents
Some research attempts to correlate the timing of solar storms with increased wildfire occurrences. While findings are mixed, certain studies suggest a possible link through impacts on electrical infrastructure and weather patterns during strong geomagnetic events.
Technological and Environmental Monitoring
Scientists use satellite data and ground measurements to monitor solar activity alongside fire incidents. This integrated approach helps improve understanding of how solar storms might contribute to increased fire risk and guides development of mitigation strategies.
Ongoing scientific research is crucial for clarifying the influence of solar storms on wildfires and enhancing preparedness efforts.
community preparedness in fire-prone areas
Community preparedness in fire-prone areas is essential to reduce risks and protect lives and property. Local residents, governments, and organizations must work together to create effective strategies.
Creating Awareness and Education
Educating communities about fire risks and safety measures helps people understand how to prevent fires and respond during emergencies. Workshops, drills, and informational campaigns are vital tools.
Developing Evacuation Plans
Well-planned evacuation routes and clear communication systems ensure residents can leave safely when fires occur. Communities should practice these plans regularly and update them based on changing conditions.
Building Fire-Resistant Infrastructure
Using fire-resistant materials in homes and creating defensible spaces by clearing dry brush reduces fire spread. Communities can also invest in local firefighting resources and equipment.
Strong community preparedness increases resilience against the threat of wildfires, improving chances of survival and minimizing damage.
policy measures addressing combined risks
Policy measures addressing combined risks of solar storms and wildfires are key to protecting communities and infrastructure. Governments and agencies implement strategies to reduce vulnerabilities and enhance emergency response.
Regulating Power Grid Resilience
Policies often focus on strengthening electrical infrastructure to withstand geomagnetic disturbances. This includes upgrading transformers, improving grid design, and creating protocols for rapid shutdowns during solar storms.
Coordinated Emergency Management
Governments establish frameworks that integrate wildfire and space weather risk management. This coordination helps ensure effective communication and resource allocation during compound disaster events.
Public Awareness and Funding
Policies support educational campaigns to raise awareness about solar storm impacts and wildfire prevention. They also provide funding for research, early warning systems, and community preparedness programs.
Implementing comprehensive policy measures helps mitigate the dangerous combination of solar storms and wildfires, protecting both people and critical systems.
future research directions on solar and fire interactions
Future research on solar and fire interactions aims to better understand how space weather affects wildfire occurrence and behavior. Scientists are exploring the links between solar storms, atmospheric changes, and terrestrial fire risks in more detail.
Advanced Data Collection
Improved satellite technology and ground sensors will provide higher resolution data on solar events and environmental conditions. This information is vital for identifying patterns and causal relationships.
Interdisciplinary Approaches
Combining expertise from space science, meteorology, ecology, and emergency management can deepen insights into these complex interactions. Collaborative studies can yield more accurate predictive models.
Development of Predictive Tools
New models integrating solar storm forecasts with fire risk assessments will help communities prepare better for overlapping hazards. These tools may support real-time decision-making and resource allocation.
Continued research is essential for reducing wildfire impacts linked to solar activity and enhancing public safety and infrastructure resilience.
Understanding Solar Storms and Their Link to Fires
Solar storms can impact more than just our technology; they may influence wildfire risks too. By affecting our electrical systems, weather, and communication networks, solar storms add complexities to managing fires, especially in places like Los Angeles.
It’s important to deepen our knowledge through research and improve early warning and preparedness systems. Communities, policymakers, and scientists all play a role in reducing risks and protecting lives and property.
Staying informed and prepared can help us face these challenges better, making our cities safer against the combined effects of solar storms and wildfires.
FAQ – Solar Storm Influence on Los Angeles Fire Risks
What is a solar storm and how does it occur?
A solar storm is a burst of charged particles and electromagnetic radiation from the sun, caused by solar flares or coronal mass ejections.
Can solar storms directly cause wildfires in Los Angeles?
Solar storms do not directly cause wildfires, but they can influence conditions like power outages and weather patterns that increase fire risks.
How do solar storms affect electrical infrastructure related to fires?
Solar storms can induce electric currents that damage transformers and power lines, potentially causing outages that disrupt fire prevention and response systems.
What are Santa Ana winds and why are they important in fire seasons?
Santa Ana winds are strong, dry winds that blow toward Los Angeles, drying out vegetation and spreading fires quickly during wildfire seasons.
How can communities prepare for the combined risks of solar storms and wildfires?
Communities can prepare by developing emergency plans, educating residents, using fire-resistant materials, and supporting early warning systems for both solar storms and fires.
Are there technologies to warn about upcoming solar storms?
Yes, satellites and ground-based observatories monitor solar activity and provide early warnings to help protect infrastructure and coordinate emergency responses.
You may also like
Ensuring Medication Safety in No-Power Conditions

Gardening for Self-Sufficiency: Fresh Produce in a Solar Crisis

The Solar Storm That Almost Was: Near-Misses in History
By Nick Morales
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
Leave a Reply