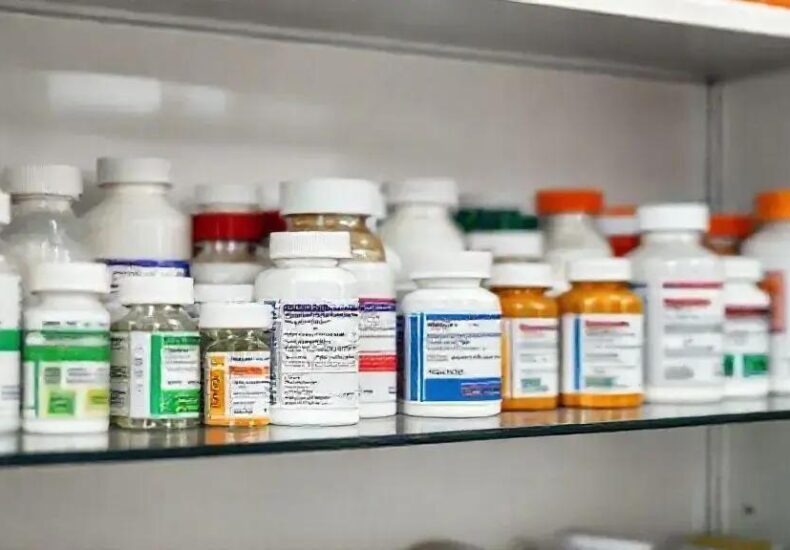

Medical Preparedness: Storing Critical Medications Without Refrigeration
Medical storage without refrigeration requires understanding medication-specific needs, using alternatives like insulated containers and desiccants, monitoring for damage, and consulting healthcare professionals to maintain medication effectiveness and safety during emergencies or power outages.
Medical Storage can be tricky when refrigeration isn t an option, but knowing how to handle medications is crucial. Ever wondered how you can keep your meds safe without a fridge? Let s explore practical tips and common practices that might surprise you.
understanding medication requirements for storage
Understanding medication requirements for storage is essential to maintaining their effectiveness and ensuring safety. Different medications have unique needs regarding temperature, humidity, and light exposure. Some require refrigeration, while others remain stable at room temperature. It is crucial to read the medication labels or consult with a healthcare provider to know the specific storage instructions.
Medications can degrade or lose potency if stored incorrectly. For example, heat-sensitive drugs might break down if exposed to high temperatures, while moisture can cause tablets or capsules to deteriorate. Additionally, certain medications are sensitive to light and should be kept in opaque containers.
By understanding these requirements, you prevent unintentional damage and ensure that your medications work as intended when needed. Always use airtight containers and keep medications in a consistent environment to avoid fluctuations that could harm the product.
Key factors affecting medication storage
The three main factors are temperature, humidity, and light. Temperature control is often the most critical; some medications require refrigeration between 2°C and 8°C, while others must stay below 25°C. Humidity should be minimized as moisture can cause chemical changes. Light sensitivity varies by medication; some require storage in dark places to prevent breakdown.
common medications that don’t require refrigeration
Many medications are designed to be stable at room temperature, making them easier to store without refrigeration. Common examples include most pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen, oral antibiotics such as amoxicillin, and many allergy medications like loratadine. These medications often come with clear storage guidelines that emphasize keeping them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Topical creams and ointments are also typically non-refrigerated but should be stored properly to prevent contamination or change in consistency. Vitamins and supplements, such as vitamin D and calcium, generally do not require refrigeration either.
Why some medications avoid refrigeration
Manufacturers formulate these medications to remain effective at varying temperatures within a typical room environment, usually 20-25°C (68-77°F). Refrigerating medications unnecessarily can sometimes reduce their effectiveness or alter their chemical makeup.
Always check the packaging or consult a pharmacist for specific advice on storage. Proper storage helps maintain medication potency and ensures patient safety.
effects of improper storage on medication efficacy
Improper storage of medications can lead to a significant decrease in their efficacy and may even pose safety risks. Medications exposed to extreme temperatures, humidity, or light can break down chemically, resulting in reduced potency or the formation of harmful byproducts. For example, heat can cause some antibiotics to lose their strength, making them less effective against infections.
Exposure to moisture can cause pills to swell, disintegrate prematurely, or stick together. This alters the intended dosage and can make the medication unsafe to use. Light-sensitive medications may degrade when exposed to sunlight or fluorescent lighting, compromising their quality.
Health risks of degraded medications
When medications lose potency, they may not provide the intended therapeutic effect. This can lead to worsening of symptoms, prolonged illness, or resistance, especially with antibiotics. Some degraded medications can become toxic or cause unexpected side effects, which is why proper storage is critical.
Checking expiration dates and storage instructions helps prevent these issues. If in doubt, consult a pharmacist before using any medication stored improperly.
alternatives to refrigeration for critical meds
When refrigeration is not an option for critical medications, there are several alternatives to help maintain their stability. Coolers with ice packs provide a temporary solution to keep meds at a lower temperature during transport or short-term storage. However, it’s important to avoid direct contact between the medication and ice packs to prevent freezing damage.
Thermal insulated bags or specialized storage containers are designed to protect medications from temperature swings by providing insulation against heat. Some containers use phase-change materials that maintain a steady temperature over several hours.
Other practical methods
Keeping medications in the coolest part of your home, such as a basement or a shaded area away from heat sources, can help maintain their integrity. Avoid storing medications in places prone to temperature fluctuations, like near windows or heating vents.
Humidity control can be achieved by using silica gel packets or moisture-absorbing packs in storage containers to prevent moisture damage.
environmental factors influencing medication stability
Environmental factors play a crucial role in the stability and effectiveness of medications. The main factors to consider are temperature, humidity, and light exposure. Each of these can impact medications differently and affect how well they work.
Temperature is one of the most important factors; too much heat can cause drugs to degrade quickly, while extreme cold can sometimes damage the medication’s structure. Humidity or moisture can lead to tablets sticking together or dissolving prematurely, reducing their potency. This is especially problematic for powders and capsules.
Light exposure, particularly UV rays from sunlight, can break down some medicines, causing chemical changes that reduce effectiveness or even create harmful side effects. That’s why some medications come in opaque or amber-colored containers to protect them from light.
Maintaining medication stability
To maintain stability, store medications in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Avoid bathrooms or kitchens where humidity fluctuates. Understanding these environmental impacts helps ensure your medications stay safe and effective when refrigeration isn’t available.
best practices for room temperature storage
Storing medications at room temperature requires following certain best practices to keep them effective and safe. Always keep medications in their original containers with labels intact to protect them from contamination and ensure clear identification.
Store medications in a cool, dry place that is away from direct sunlight, heat sources, and moisture. Avoid places like bathrooms or kitchens where humidity and temperature can fluctuate frequently.
Proper handling and organization
Organize medications so that those nearing expiration are easily accessible for timely use. Use airtight containers or zip-lock bags to protect medications from moisture. Keep medications out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion.
Regularly check expiration dates and dispose of any medications that are expired or show signs of damage such as discoloration, crumbling, or unusual odor. Following these simple steps can help maintain medication stability and safety during room temperature storage.
using specialized containers and desiccants
Using specialized containers and desiccants is an effective way to protect medications from environmental factors like moisture and air exposure, especially when refrigeration isn’t available. Specialized containers such as airtight plastic or glass bottles provide a barrier against humidity and contaminants.
Desiccants, commonly found as small packets inside medication packaging, absorb moisture and help keep the environment dry. They are especially useful for medications sensitive to humidity, such as powders, capsules, and tablets.
Choosing the right storage aids
When reusing containers, ensure they are clean, airtight, and compatible with the medication stored. Use new desiccant packets as old ones become saturated and lose effectiveness. Additionally, consider containers with built-in temperature and humidity indicators for better monitoring.
Combining these tools helps maintain medication stability and potency, reducing the risk of degradation and extending shelf life during room temperature storage.
monitoring and identifying compromised medications
Monitoring and identifying compromised medications is vital to ensure safety and effectiveness. Medications that have been stored improperly or are past their expiration date can lose potency or become harmful. Look for changes such as discoloration, unusual odors, crumbling tablets, or separation in liquids, which often indicate degradation.
Regularly check expiration dates and avoid using medications beyond that time. If you notice any physical changes or if the medication has been exposed to extreme temperatures or moisture, it’s best to discard it safely and consult a healthcare professional for a replacement.
How to monitor medication condition
Use a dedicated storage area that is clean, dry, and organized to keep track of your medications. Keep an inventory list and date when medications were first opened. Consider using labels or color codes to separate new from older supplies, making it easier to identify what needs attention.
planning for emergencies and power outages
Planning for emergencies and power outages is essential when storing critical medications that typically require refrigeration. Start by identifying which medications can safely be stored at room temperature and which truly require cold storage. Keep an updated list of these medications and their specific storage needs.
Investing in alternative cooling options such as portable battery-powered coolers or insulated thermal bags can provide temporary refrigeration during power disruptions. Additionally, having ice packs and coolers on hand can help maintain necessary temperatures for short periods.
Emergency preparedness tips
Keep medications organized and easily accessible to minimize exposure time during transfers. Communicate your medication needs to family members or caregivers to ensure quick action if power is lost. Consider registering with local emergency services that offer assistance during outages, especially for those reliant on refrigerated medications.
Regularly check and replace ice packs or batteries to ensure readiness. Establish a plan for safely disposing of any medications that become compromised due to temperature fluctuations during emergencies.
consulting healthcare professionals about medication storage
Consulting healthcare professionals about medication storage is a crucial step to ensure your medications remain safe and effective. Pharmacists and doctors can provide specific guidance based on the type of medication, its sensitivity, and your personal circumstances.
Healthcare professionals can clarify whether a medication truly requires refrigeration or if there are safe alternatives, helping you avoid unnecessary cooling that could damage the product. They can also advise on how to manage storage during travel, power outages, or emergencies.
Why professional advice matters
Medications can have complex storage needs that vary widely. A healthcare provider’s input helps prevent medication errors and ensures optimal treatment outcomes. They can also help you interpret product labels and provide tips to recognize when a medication might be compromised.
Regular consultations allow you to stay updated on any changes in storage recommendations or new products that could offer easier management. Always seek professional advice when in doubt about how to store your medications safely.
Ensuring Safe Medication Storage Without Refrigeration
Proper storage of medications is key to maintaining their effectiveness and safety, especially when refrigeration isn’t an option. By understanding medication needs, using alternatives like insulated containers, and following best practices for room temperature storage, you can safeguard your treatments.
Remember to monitor your medications regularly and seek advice from healthcare professionals when unsure. Planning ahead for emergencies and power outages also helps protect your critical meds.
Taking these steps ensures your medications remain reliable when you need them most, supporting your health and well-being.
FAQ – Common Questions About Medical Storage Without Refrigeration
Can all medications be stored without refrigeration?
No, only certain medications that are stable at room temperature can be stored without refrigeration. Always check the label or consult a healthcare professional.
What are some alternatives to refrigeration for storing medications?
Alternatives include insulated bags, portable coolers with ice packs, airtight containers, and using desiccants to control moisture.
How does improper storage affect medication effectiveness?
Improper storage can cause medications to lose potency, degrade chemically, or become unsafe due to moisture, heat, or light exposure.
How can I tell if my medication has been compromised?
Signs include changes in color, texture, smell, or if tablets are crumbling or liquids are cloudy. Always check expiration dates as well.
What should I do during a power outage if my medication requires refrigeration?
Use insulated coolers or portable battery-powered refrigeration units. Keep ice packs ready and plan ahead to maintain medication temperature during outages.
Why is consulting a healthcare professional about medication storage important?
Healthcare professionals provide guidance specific to your medication type and circumstances, helping ensure safe storage and effective treatment.
You may also like
Ensuring Medication Safety in No-Power Conditions

The Role of Local Authorities and How to Stay Informed

By Nick Morales
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
Leave a Reply