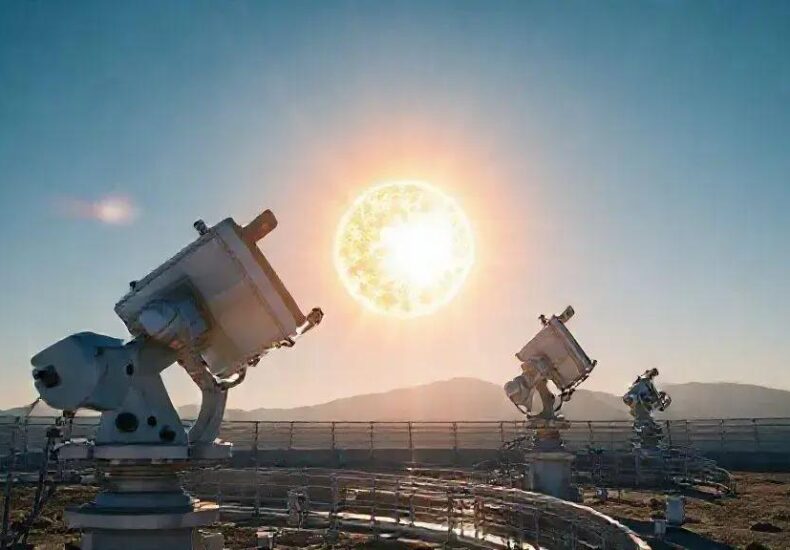

The Solar Observatory Report: Fresh Imagery Reveals New Clues
Solar Observatory uses advanced telescopes and sensors to capture detailed images and data of the sun, enabling real-time monitoring, solar research, and space weather forecasting to protect Earth’s technology and improve scientific understanding.
Solar Observatory updates are exciting, right? Imagine catching fresh sun images that might just rewrite what we know about our star. Curious about what new solar secrets these snapshots reveal? Let’s dig in and explore together.
how the solar observatory captures detailed sun imagery
The solar observatory uses advanced telescopes equipped with special filters to capture highly detailed images of the sun. These filters block harmful solar radiation while allowing specific wavelengths of light to pass through, revealing various solar features.
High-resolution solar telescopes
Modern solar telescopes have large apertures that collect more light, enabling clearer and sharper images. They often use adaptive optics technology, which adjusts for the Earth’s atmospheric distortions, ensuring a precise observation of solar structures.
Specialized imaging techniques
The observatories employ techniques like spectroscopy and narrowband imaging to focus on different layers of the solar atmosphere. This helps scientists study sunspots, solar flares, and prominences in great detail and understand their behavior.
Data processing and enhancement
After capturing raw images, specialist software processes the data to enhance details and reduce noise. This step is crucial for highlighting subtle features that are invisible to the naked eye, providing researchers with valuable insights.
By combining sophisticated technology and image-processing methods, the solar observatory delivers remarkably detailed pictures of the sun, deepening our understanding of its complex dynamics.
recent discoveries from the latest solar scans
Recent solar scans have unveiled fascinating new details about the sun’s surface and atmosphere. Using high-resolution imaging, scientists observed unexpected magnetic field patterns that could explain sudden solar storms.
Uncovering magnetic mysteries
The latest observations revealed complex magnetic loops that twist and interact in ways previously unknown. These loops can store vast amounts of energy, which might be released suddenly as solar flares, impacting space weather.
Insights into solar flares and coronal mass ejections
Data from new solar scans helped researchers identify the early signs of powerful solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). Understanding these signs improves forecasting and helps protect satellites and astronauts from radiation risks.
Solar atmosphere temperature variations
Scientists detected surprising temperature differences in the solar corona, suggesting different heating mechanisms at play. These findings challenge old models and push for new research to uncover the sun’s heating processes.
The latest solar scans are revolutionizing how we perceive our star’s activity and behavior, providing valuable clues for both science and technology.
technology behind solar observation instruments
Solar observation instruments rely on cutting-edge technology to study the sun with precision. These tools include specialized telescopes, spectrometers, and imaging devices designed to capture a wide range of solar phenomena.
Solar telescopes and adaptive optics
Modern solar telescopes are equipped with adaptive optics systems that correct atmospheric distortions in real time. This technology produces clearer images, allowing scientists to observe fine solar details such as sunspots and solar granulation.
Spectrometers for solar analysis
Spectrometers analyze the sun’s light spectrum, helping researchers identify chemical elements and measure temperature and velocity of solar material. This information is essential for understanding solar activity and composition.
High-resolution imaging sensors
Advanced charge-coupled devices (CCDs) and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) sensors capture high-resolution images. These sensors are sensitive to various wavelengths, enabling a comprehensive view of the sun’s layers.
Data handling and processing
The vast amount of data gathered is processed using powerful computers. Algorithms enhance image quality and extract meaningful patterns, improving the study of dynamic solar processes.
Together, these technologies allow solar observatories to continuously monitor and decode the complex behavior of our star.
understanding solar flares and their impact
Solar flares are sudden bursts of light and energy from the sun’s surface caused by magnetic activity. These powerful explosions release radiation across the entire electromagnetic spectrum, including X-rays and ultraviolet rays.
How solar flares form
Solar flares occur when twisted magnetic fields near sunspots suddenly realign. This magnetic reconnection releases huge amounts of energy in seconds, heating solar material to millions of degrees.
Effects of solar flares on Earth
When solar flare radiation reaches Earth, it can disrupt satellite communications, GPS signals, and radio transmissions. Strong flares can also cause beautiful auroras by interacting with Earth’s magnetic field.
Impact on technology and space travel
Solar flares pose risks to astronauts by exposing them to high radiation levels. They can also harm satellites and power grids, causing blackouts and equipment failures. Monitoring flares helps prepare and protect critical systems.
Understanding solar flares is essential for space weather forecasting and minimizing their harmful effects on modern technology and human activities.
role of observatories in space weather forecasting
Observatories play a vital role in forecasting space weather by continuously monitoring solar activity and its effects on Earth’s environment. They gather detailed data on solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and solar wind conditions.
Real-time solar monitoring
Solar observatories use advanced instruments to provide real-time alerts of solar events. This helps predict geomagnetic storms that can disrupt communication and power systems on Earth.
Data collection and analysis
Observatories collect vast amounts of data, which is analyzed to understand patterns in solar activity. This analysis supports accurate forecasts and early warning systems for potentially harmful solar events.
Supporting satellite and aviation safety
Space weather forecasts provided by observatories help protect satellites and aircraft by predicting increased radiation levels. This information allows operators to take preventive measures to avoid damage or health risks.
By combining continuous observation and sophisticated data processing, observatories form the backbone of modern space weather forecasting systems.
how solar data influences satellite safety
Solar data plays a crucial role in ensuring satellite safety by providing early warnings of solar storms and other space weather events. These events can disrupt satellite operations and cause damage to sensitive electronic components.
Monitoring solar activity for risk assessment
By analyzing solar flares and coronal mass ejections, scientists can predict periods of increased radiation that may harm satellites. This information helps satellite operators prepare and take protective measures.
Shielding satellites from solar radiation
Satellites can be temporarily placed into safe modes during intense solar activity to reduce exposure to harmful radiation. Data from solar observatories guides these decisions to minimize damage.
Maintaining communication and navigation systems
Solar events can interfere with GPS signals and communication satellites. Real-time solar data allows operators to adjust signal paths and maintain service reliability during solar disruptions.
Integrating solar data into satellite operations is essential for preventing outages and extending the functional life of space assets.
amateur astronomy and the solar observatory
Amateur astronomers often play a key role in supporting solar observatories by contributing observations and data. With advances in technology, enthusiasts have access to high-quality telescopes and cameras that can capture solar features like sunspots and prominences.
Collaboration opportunities
Many solar observatories encourage amateurs to share their findings through online platforms. This crowdsourced data can complement professional research and help track solar activity in real time.
Accessible solar observing equipment
Affordable solar filters and dedicated solar telescopes enable amateurs to safely observe and photograph the sun. These tools open the door to learning and engaging more deeply with solar science.
Educational benefits
Engaging in solar observation helps amateurs understand solar dynamics and space weather. This hands-on experience often inspires further interest in astronomy and science careers.
Amateur astronomers enrich solar research by making observations more frequent and widespread, creating a valuable bridge between the public and professional science.
collaboration between observatories worldwide
Collaboration between observatories worldwide enhances our understanding of the sun by sharing data and resources. This teamwork allows scientists to combine observations from different locations and instruments to get a complete picture of solar activity.
Global data networks
Observatories connect through networks that share real-time solar data. This connectivity helps track solar events as they evolve, improving forecasting accuracy.
Joint research projects
Scientists from various observatories collaborate on projects to study solar phenomena, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections. These joint efforts pool expertise and technology to push the boundaries of solar science.
Resource and knowledge exchange
Sharing technologies, software, and findings accelerates innovation in solar observation. Training programs and conferences foster knowledge transfer among international teams.
This global cooperation greatly advances our ability to monitor and understand the sun, benefiting science and technology worldwide.
future missions inspired by solar observations
Future missions inspired by solar observations aim to deepen our knowledge of the sun and its influence on the solar system. These missions focus on advanced technology to explore solar phenomena more closely and comprehensively.
Next-generation solar probes
Upcoming missions will send spacecraft closer to the sun than ever before, equipped with highly sensitive instruments to measure magnetic fields, solar wind, and energetic particles.
Enhanced imaging and spectroscopy
Future solar observatories will use cutting-edge imaging sensors and spectrometers to capture more detailed solar activity, helping to unravel the mysteries of solar flares and coronal heating.
International partnerships
Collaborations between space agencies worldwide will pool resources and expertise. These partnerships increase mission scope and data sharing, enhancing scientific outcomes.
These forward-looking missions represent a leap in solar science, promising new insights and better space weather forecasting to protect Earth’s technology and climate.
challenges in maintaining observatory equipment
Maintaining observatory equipment presents several challenges due to the complexity and precision required. Solar observatories rely on sensitive instruments that must be kept in perfect condition to produce accurate data.
Environmental exposure
Observatories face harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, dust, and humidity. These elements can degrade equipment components and alter instrument calibration, requiring regular maintenance and protection measures.
Precision alignment and calibration
Telescopes and sensors need frequent calibration to maintain accuracy. Small misalignments can significantly affect data quality, so technicians carefully adjust optical components and electronic systems.
High costs and technical expertise
Upkeep demands specialized skills and expensive parts. Trained engineers and scientists often work together to troubleshoot and upgrade equipment, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Despite these challenges, ongoing maintenance is essential to ensure that solar observatories continue to provide valuable scientific insights.
Understanding the Importance of Solar Observatories
Solar observatories provide invaluable data that help us better understand the complex nature of our sun. Despite challenges in maintaining advanced equipment, the insights gained from these observatories drive scientific progress.
By monitoring solar activity and collaborating globally, researchers can predict space weather and protect our technology. This ongoing effort is essential for advancing knowledge and safeguarding our modern world.
Investing in the maintenance and development of solar observation technology ensures that we continue to reveal new solar mysteries and improve our ability to respond to solar events.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Solar Observatories
What is the primary function of a solar observatory?
A solar observatory monitors and studies the sun’s activity, capturing detailed images and data to understand solar phenomena and space weather.
How does solar activity affect Earth?
Solar activity, like solar flares and coronal mass ejections, can disrupt satellite communications, GPS signals, and power grids on Earth.
Why is collaboration between observatories important?
Collaboration allows global sharing of data and resources, improving accuracy in solar monitoring and forecasting space weather events.
What challenges do observatories face in maintaining equipment?
Observatories face issues like environmental exposure, high maintenance costs, and the need for precise calibration of sensitive instruments.
How can amateur astronomers contribute to solar observations?
Amateurs can contribute by using solar telescopes and sharing observations, which supplements professional data and helps track solar activity more frequently.
What role does solar data play in satellite safety?
Solar data helps predict harmful solar events, allowing operators to safeguard satellites by adjusting operations and limiting radiation exposure.
You may also like

Latest Research Papers: Innovations in Solar Forecasting

Surge in Aurora Sightings: Best Viewing Spots Right Now
By Nick Morales
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | |
Leave a Reply