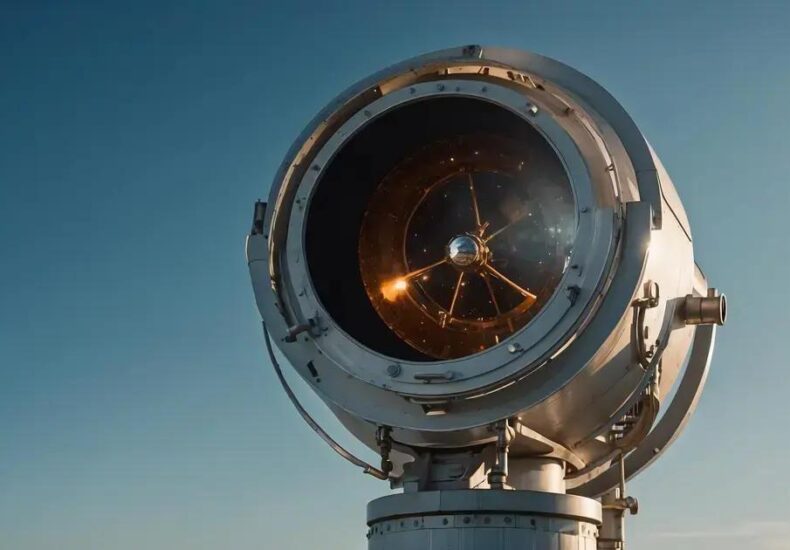

State-of-the-Art Telescopes: Sharper Views of Solar Activity
Telescopes Views provide detailed observations of solar activity by using advanced optics, space-based platforms, and adaptive technologies to capture high-resolution images of solar flares, sunspots, and storms essential for research and space weather prediction.
If you’ve ever been curious about the fiery dance happening on the sun, Telescopes Views gives a clearer window into solar activity than ever before. Imagine the details we’re now able to see—from solar flares to sunspots—thanks to powerful, state-of-the-art telescopes.
how modern telescopes capture solar activity in detail
Modern telescopes use advanced optical systems and sensors to capture solar activity with remarkable precision. High-resolution cameras and specialized filters allow these instruments to observe phenomena such as sunspots, solar flares, and prominences in great detail.
Advanced Optics and Sensors
These telescopes are equipped with adaptive optics that adjust for atmospheric distortions, ensuring clearer images. Sensors like CCD (charge-coupled device) detectors convert light into digital images, capturing subtle variations in solar emissions.
Specialized Filters
Filters tuned to specific wavelengths, such as hydrogen-alpha or ultraviolet, highlight different layers and activities on the sun’s surface. This helps scientists study magnetic field changes and eruption patterns.
Data Processing and Imaging
The raw data collected undergoes sophisticated processing to enhance clarity and contrast. This enables researchers to analyze solar events frame by frame, improving understanding of their causes and effects.
With these technologies combined, modern telescopes provide a window into the dynamic processes of the sun, offering insights crucial for space weather forecasting and solar physics research.
technological advances boosting telescope resolution
Telescope resolution has greatly improved thanks to technological advances that allow scientists to see the sun and other celestial bodies with more detail than ever before. One key development is adaptive optics, which corrects distortions caused by Earth’s atmosphere in real-time.
Adaptive Optics
This technology uses deformable mirrors and sensors to constantly adjust the telescope’s optics, leading to much sharper images. It helps remove the blurriness that typically occurs when observing from the ground.
Interferometry
Another breakthrough is interferometry, where multiple telescopes work together to simulate a much larger telescope. By combining their signals, astronomers achieve higher resolution and can detect finer details of solar activity.
Advanced Detectors and Instruments
Modern detectors, like high-sensitivity CCD and CMOS sensors, enhance the ability to record faint solar features. Instruments tailored to capture different wavelengths of light also help reveal hidden structures in the sun’s atmosphere.
Together, these advances contribute to a sharper and clearer view of solar events, enabling better research and understanding of the sun’s behavior.
understanding solar flares through enhanced views
Solar flares are sudden bursts of energy on the sun’s surface that release massive amounts of light and radiation. Enhanced views from advanced telescopes help scientists study these powerful eruptions in detail.
What Causes Solar Flares?
Solar flares occur when magnetic energy stored in the sun’s atmosphere is suddenly released. Twisted magnetic field lines snap and reconnect, producing intense bursts of radiation that can last minutes to hours.
How Enhanced Views Improve Understanding
Modern telescopes that observe in multiple wavelengths—such as X-rays, ultraviolet, and visible light—give a complete picture of flare development. These instruments reveal the changing structure and motion of plasma during a flare.
Tracking Flare Effects
High-resolution images allow researchers to track how solar flares impact space weather, including solar wind and energetic particles. This helps predict potential disruptions to satellites and communication systems on Earth.
Thanks to sharper telescope views, scientists can better analyze the timing, size, and impact of solar flares, deepening our knowledge of the sun’s behavior.
the role of space-based telescopes in solar observation
Space-based telescopes have transformed the study of the sun by removing the distortions caused by Earth’s atmosphere. Positioned above the atmosphere, these instruments capture crystal-clear images and data on solar activity.
Uninterrupted Observation
Without atmospheric interference, space telescopes can observe the sun continuously and across many wavelengths, including ultraviolet and X-rays, which do not penetrate Earth’s atmosphere. This provides a fuller understanding of solar processes.
Examples of Space Telescopes
Telescopes like the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) have been crucial for solar research. They provide real-time monitoring of solar flares, sunspots, and coronal mass ejections.
Impact on Space Weather Prediction
Data from space-based telescopes improve the accuracy of space weather forecasts. This information is vital to protect satellites, power grids, and communication systems on Earth from solar storms.
Overall, space-based telescopes offer unparalleled clarity and coverage, making them indispensable tools for understanding and predicting solar behavior.
ground-based versus space telescopes: pros and cons
Ground-based telescopes and space telescopes each offer unique advantages and face certain challenges when observing solar activity. Understanding these pros and cons helps clarify their roles in solar research.
Pros of Ground-Based Telescopes
Ground telescopes can be larger and more easily maintained or upgraded. They often have lower costs compared to space telescopes and can be built with cutting-edge adaptive optics technology to reduce atmospheric distortion.
Cons of Ground-Based Telescopes
These telescopes must contend with atmospheric effects like turbulence and weather conditions, which can blur images and limit observation time. They also cannot observe certain wavelengths like ultraviolet and X-rays that are blocked by Earth’s atmosphere.
Pros of Space Telescopes
Space telescopes operate above the atmosphere, providing uninterrupted, clear views across all wavelengths. This allows the study of solar phenomena in ultraviolet, X-rays, and other bands inaccessible from Earth.
Cons of Space Telescopes
They are expensive to build and launch, with limited opportunities for repair or upgrades after deployment. Operational lifespans are finite due to harsh space conditions and fuel limitations.
Each type complements the other, with ground-based systems offering flexibility and accessibility, while space telescopes provide unmatched clarity and coverage for solar observations.
how telescope data helps predict solar storms
Telescope data plays a crucial role in predicting solar storms by providing detailed information about solar activity such as flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). These events can have significant impacts on Earth’s magnetic field and technology.
Monitoring Solar Activity
Telescopes track changes on the sun’s surface and atmosphere, capturing high-resolution images and spectra that reveal the intensity and evolution of active regions. This data allows scientists to identify potentially dangerous flares and CMEs early.
Analyzing Magnetic Fields
Precise observations help map the sun’s magnetic field structure, which is key to understanding when and where solar storms might erupt. Changes in magnetic configurations are strong indicators of impending solar eruptions.
Modeling and Forecasting
Combining telescope data with computer models, researchers simulate the path and impact of solar storms as they travel through space toward Earth. This forecasting helps to predict the timing and severity of geomagnetic disturbances.
Overall, telescope data provides the critical insights needed for early warnings to protect satellites, power grids, and communication networks from solar storm effects.
challenges in observing solar phenomena clearly
Observing solar phenomena clearly presents several challenges due to the sun’s intense brightness and the Earth’s atmospheric conditions. These factors can distort or block important details needed for accurate analysis.
Atmospheric Distortion
The Earth’s atmosphere causes turbulence and blurring, which reduce the clarity of ground-based telescope images. This problem is known as “seeing” and can vary with weather and location.
Solar Brightness
The sun’s brightness is so intense that specialized filters and instruments are necessary to observe features like flares or sunspots without damaging sensors or overwhelming images.
Limitations in Wavelength Observation
Certain wavelengths emitted by solar phenomena, such as ultraviolet and X-rays, are absorbed by the atmosphere. This limits the capabilities of ground telescopes, requiring space-based observatories for complete observation.
Instrumentation and Calibration
High-end equipment must be precisely calibrated to detect subtle solar details. Even minor errors can lead to misleading data or missed events.
Researchers continuously develop techniques like adaptive optics and space missions to overcome these observation challenges and enhance our understanding of the sun.
future innovations in telescope design for solar studies
Future innovations in telescope design for solar studies focus on improving resolution, sensitivity, and adaptability to capture the sun’s dynamic activity better. These advancements will enable more detailed and accurate observations.
Next-Generation Adaptive Optics
Improved adaptive optics systems will better correct atmospheric distortions, allowing ground-based telescopes to achieve near space-quality images. These systems use faster sensors and smarter algorithms.
Lightweight and Flexible Materials
Innovations in materials science lead to lighter, stronger mirrors and telescope structures. This helps build larger telescopes that can be easier to deploy, especially in space missions.
Multi-Wavelength and Multi-Sensor Integration
Future telescopes are designed to integrate various sensors that capture solar emissions across different wavelengths simultaneously. This integration offers a comprehensive view of solar phenomena in real-time.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI-driven data processing and automated control systems will enhance the speed and accuracy of solar observations, enabling telescopes to react quickly to transient solar events like flares.
These innovations promise to push the boundaries of solar research, improving our understanding of the sun and its effects on Earth.
practical ways to access and use solar telescope data
Accessing and using solar telescope data has become easier thanks to technological advances and open data policies. Both researchers and enthusiasts can explore detailed solar information online to study or enjoy solar phenomena.
Online Data Portals
Many organizations, such as NASA and the European Space Agency, provide free access to solar telescope data through online portals. Users can download images, videos, and scientific measurements from missions like the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
Data Analysis Tools
Several software tools and apps allow users to analyze and visualize solar data. These applications can generate timelapse videos, track solar events, and interpret magnetic field maps for a better understanding of solar activity.
Educational Resources
Online tutorials and forums help beginners learn how to work with solar data. They offer step-by-step guides on downloading data, using analysis software, and understanding solar phenomena through real telescope observations.
By leveraging these resources, anyone can gain valuable insights into the sun’s activity and contribute to solar research or simply enjoy the stunning views offered by modern solar telescopes.
Understanding the Sun with Advanced Telescopes
Modern telescopes provide sharper views of solar activity, helping us explore the sun’s powerful and changing nature in great detail.
From ground-based optics to space observatories, each tool offers unique ways to watch solar flares, sunspots, and storms that affect Earth.
With ongoing innovations and open access to solar data, both scientists and enthusiasts can deepen their knowledge and stay informed about solar events.
By embracing these advances, we gain valuable insights that improve space weather predictions and protect our technology-dependent world.
FAQ – Understanding Advanced Telescopes and Solar Observation
What makes space-based telescopes better for solar observation?
Space-based telescopes avoid atmospheric distortions, allowing them to capture clearer images across wavelengths like ultraviolet and X-rays that can’t be seen from Earth.
How do adaptive optics improve ground-based telescope images?
Adaptive optics correct distortions caused by Earth’s atmosphere in real-time, making images sharper and clearer despite atmospheric turbulence.
Why is it important to monitor solar flares and storms?
Solar flares and storms can disrupt satellites, power grids, and communication systems on Earth, so monitoring them helps in predicting and mitigating their impacts.
Can anyone access solar telescope data?
Yes, many organizations provide free access to solar telescope data online, allowing researchers and the public to explore solar activity.
What challenges do telescopes face when observing the sun?
Challenges include atmospheric distortion for ground telescopes, the sun’s intense brightness, and the inability to observe certain wavelengths from Earth’s surface.
How will future telescopes improve solar studies?
Future telescopes will feature better adaptive optics, lightweight materials, multi-wavelength sensors, and AI-driven automation to capture more detailed and accurate solar data.
You may also like
Ensuring Medication Safety in No-Power Conditions

The Solar Observatory Report: Fresh Imagery Reveals New Clues

Gardening for Self-Sufficiency: Fresh Produce in a Solar Crisis
By Nick Morales
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
Leave a Reply